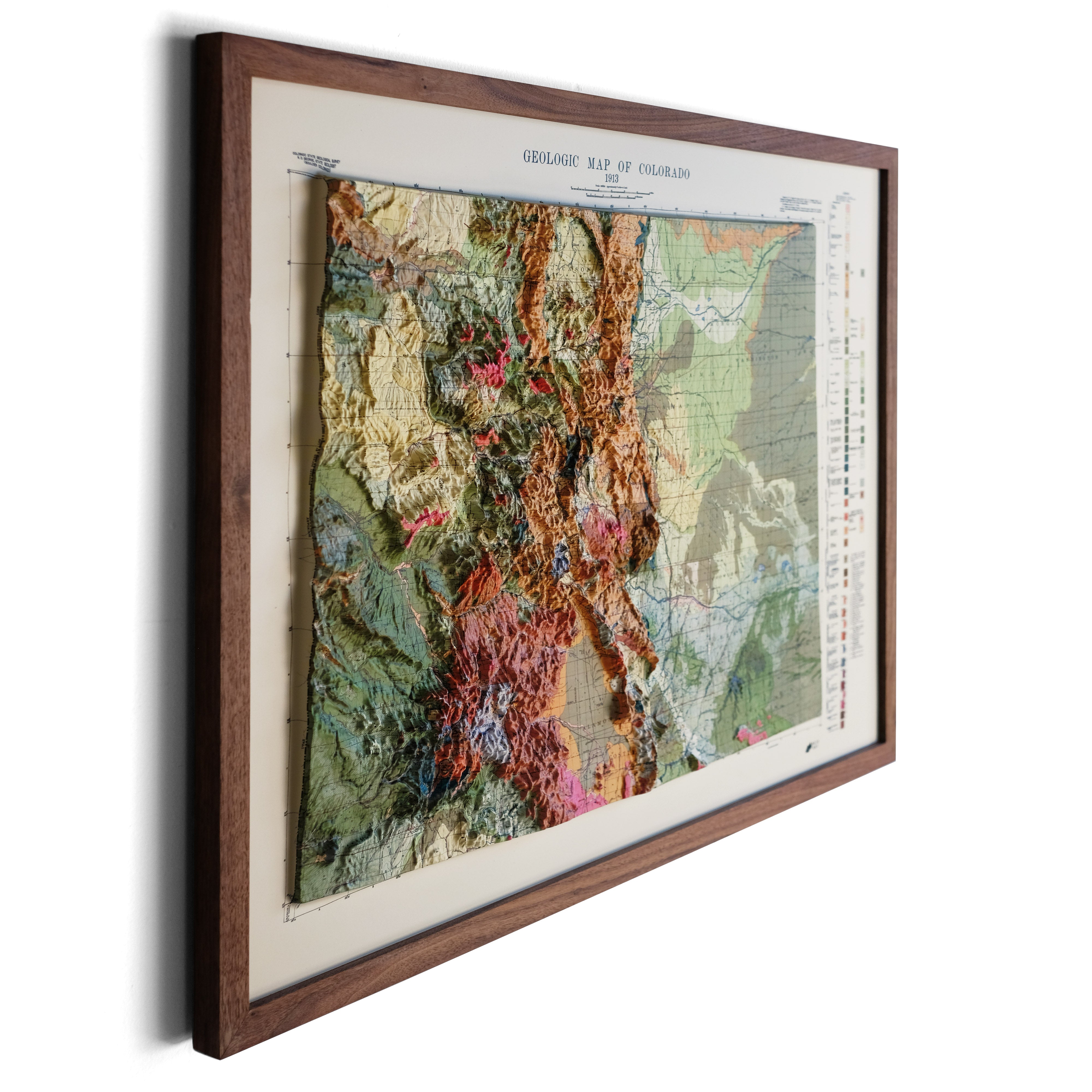
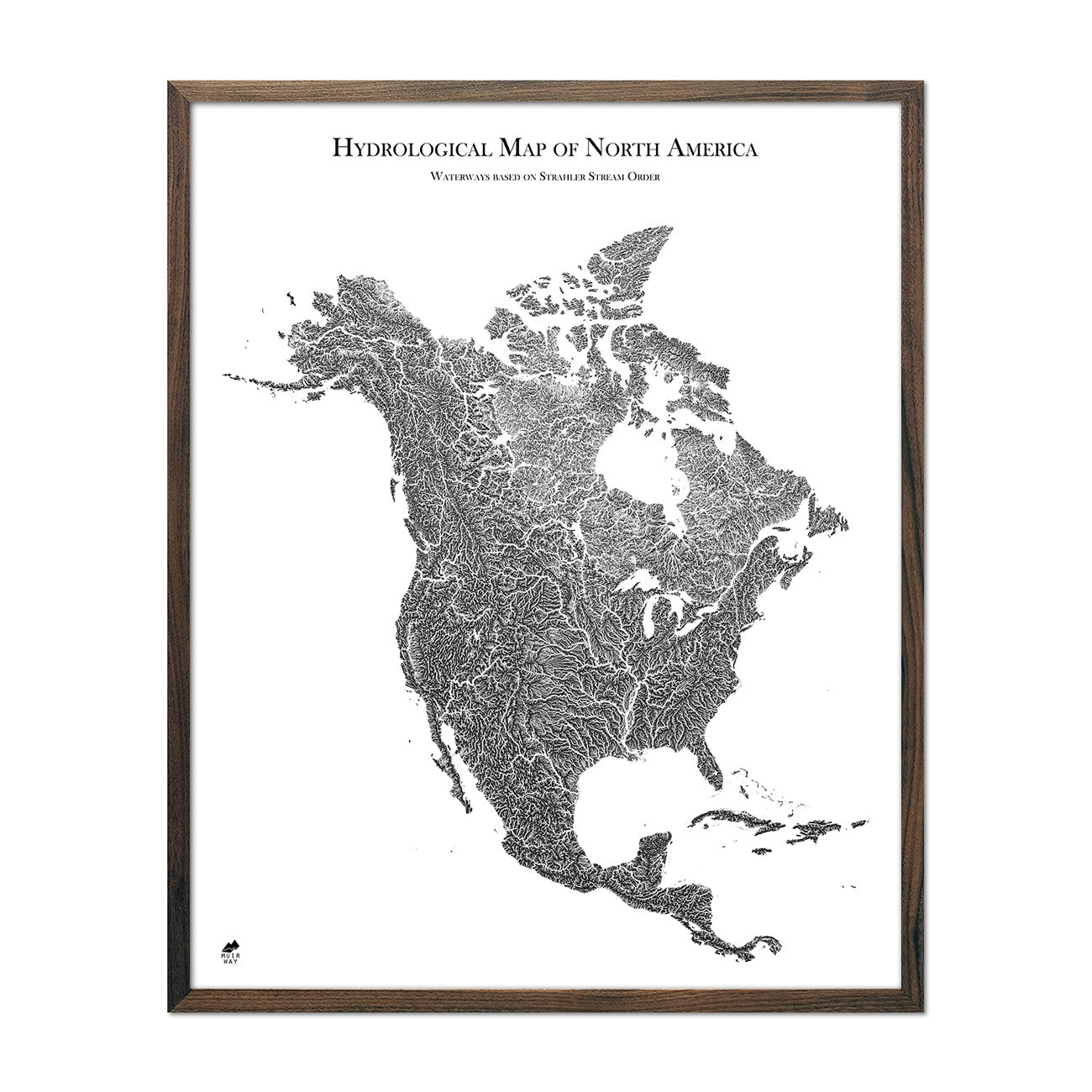
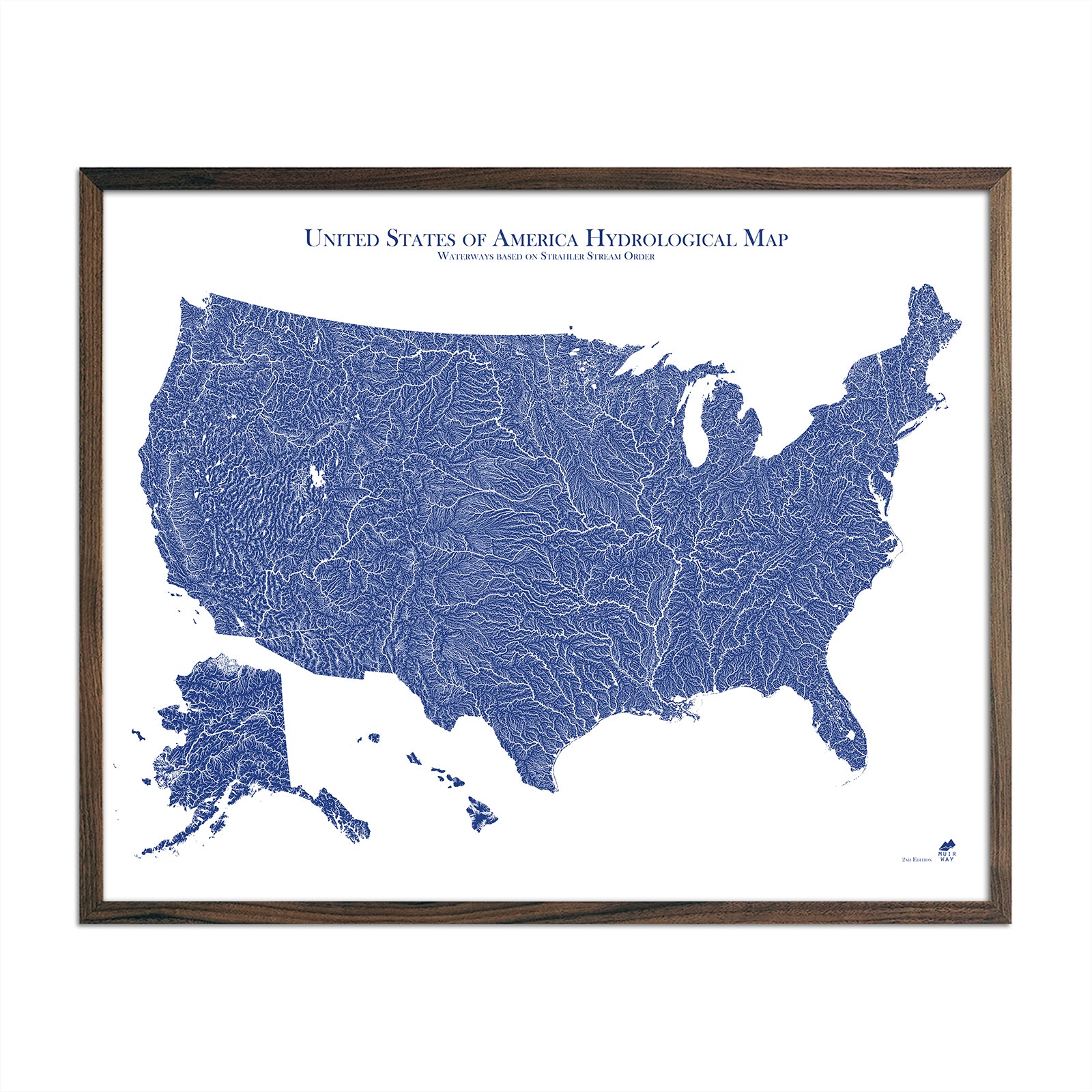
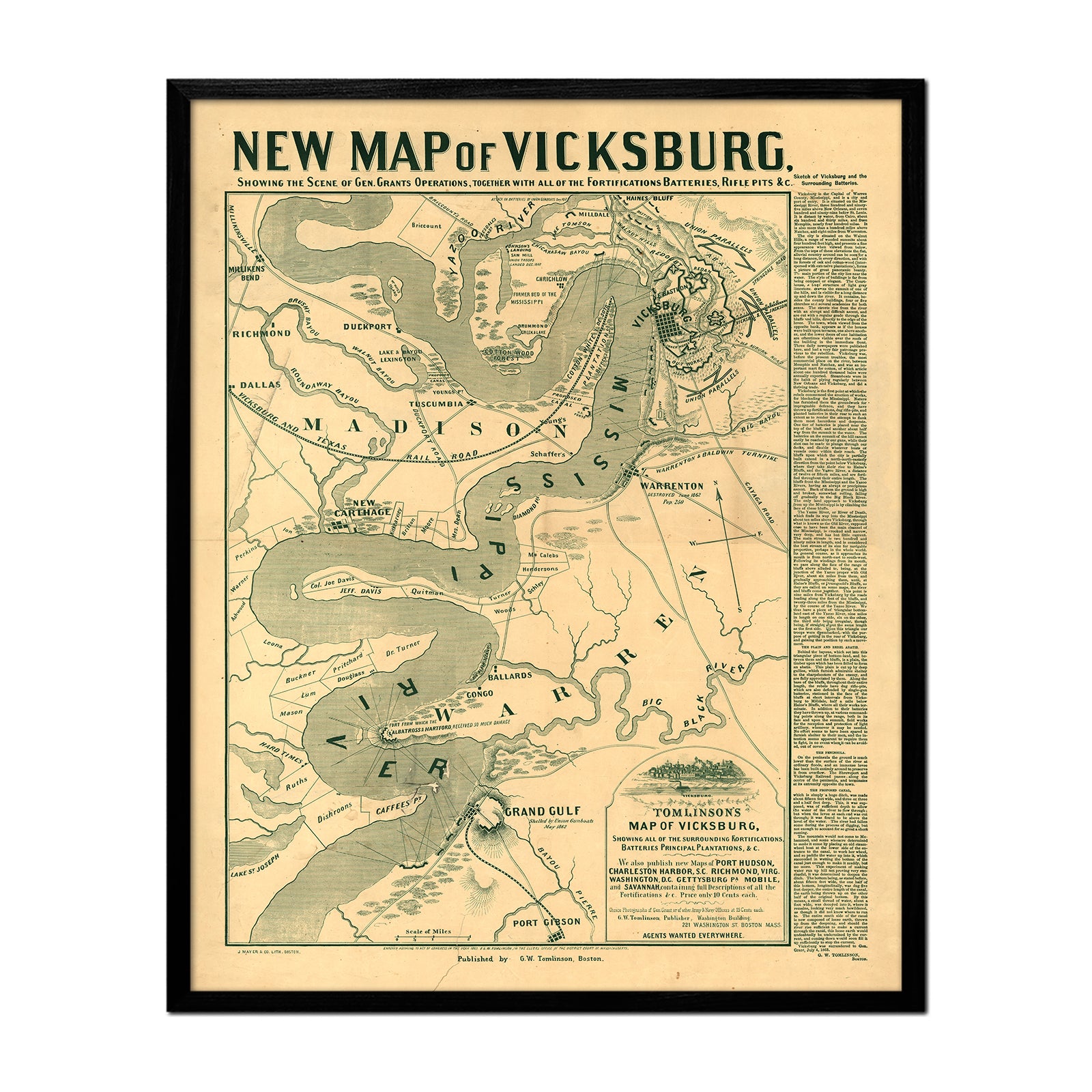
What is a topographic map?
A topographic map is a two-dimensional representation of the Earth’s surface, revealing both natural and artificial features. One of the most popular types of maps, topographic maps use elevation contour lines - connecting points of equal elevation - to show undulations in terrain that define various geological features such as mountains, hills, ridges, depressions, valleys, and all other aspects of the earth’s surface. Watercourses and waterbodies are also indicated. Topographic maps include man-made features, like larger buildings, farmsteads, orchards, urbanized areas, roads, and railways.

The History of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps have evolved over time for various purposes. In 1789, France was the first to complete a multi-page topographic map series of an entire country; the Carte géométrique de la France2. The East India Company successfully recorded accurate height measurements of the Himalayan Mountains in the Great Trigonometric Survey of India in 1871. The United Kingdom utilized topographic surveys to strategize for battle, plan infrastructure, and capitalize resources. In 1879, the merging of the Army Corps of Engineers and the Department of the Interior birthed the United States Geological Survey (USGS), which is responsible for overseeing United States land, natural resources, and threats to the nation's environment.


How Topographic Maps are Made
Topographic map technology used today
Developing technologies during the 1980s popularized the use of computerized databases instead of traditional, printed topographic maps. In the United States, Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Reference (TIGER) and Digital Elevation Model (DEM) information were compiled and made a public domain, user-friendly resource, available online. NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory have published the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) DEM dataset, which covers the earth’s entire surface from the equator to 60°N/S at 10m resolution or better.
Topographical surveying to collect topographic map data
The data used to create topographic maps are based on topographical surveys. Topographical land surveys show the height, depth, size, location, and elevation of objects and land features of a specific area. Historically, topographic surveying involved the use of primitive tools during risky and expensive excursions. Early surveying incorporated a classic mapping technique known as plane table surveying4, used until the 1940s, which involved hand plotting of land features, measured in the field from a vantage point, using a sighting device. Airplanes revolutionized previous mapping methods by introducing aerial photographs and photogrammetry5, which obtained information from analyzing and measuring aerial images. These airborne techniques reformed map-making by increasing map coverage, elevating cartographic standards, improving accuracy, and efficiently cutting down on production time. Today, USGS incorporates digital datasets into computer-based applications such as geographic information systems (GIS) and global positioning systems (GPS) to better capture, analyze, and represent spatial information used in topographic maps.


Topographic map series
Topographic maps series are made of multiple map sheets that form part of a larger series, often covering an entire nation. A map series will share specifications, including map symbols, map projection, coordinate system, ellipsoid, geodetic datum, and a national grid referencing system. The US Geological Survey (USGS) is one of the leading agencies when it comes to producing national topographic maps, providing numerous series at various scales. The main USGS topographical series of maps 6, 7 use a 1:24,000 scale and cover a quadrangle that measures 7.5-minutes (49 to 70 square miles) of longitude and latitude on all sides. This series divides the United States into uniform quadrangles that inform the mapping index system.
Topographic maps continue to be improved with the development of technology. Today, these maps are essential to earth science studies, the built-environment and construction, geographic planning, urban planning, extracting resources (mining, logging, farming, etc.), engineering, and recreation (hiking, camping, etc.).


View our TOPO Series collection of maps, showcasing popular mountains and ski destinations in a way you’ve never seen them before. Also see our Relief Series, showcasing beautiful USGS relief mosaics of popular natural wonders from around the country.
Source:
https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-a-topographic-map?qt-news_science_products=0#qt-news_science_products
https://carrollengineering.com/topographic-surveys-what-you-need-to-know/
Image Source:
- https://www.hcs.stier.org/Downloads/Dimensions%20of%20Earth%20Multiple%20Choice.pdf
- https://www.loc.gov/resource/g5830.ct001183/
- https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10.1098/rsnr.2020.0052
- https://geodesy.noaa.gov/INFO/history/plane-table.shtml
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/phor.12277
- https://ngmdb.usgs.gov/topoview/viewer